BMI Calculator
Use our BMI calculator below to quickly determine your Body Mass Index. Simply enter your height and weight to get your results instantly.
Your Comprehensive Health Report
Basic Information
Age:
Gender:
Height:
Weight:
BMI Results
BMI:
Category:
Ideal Weight Range:
Energy & Metabolism
BMR: calories/day
TDEE: calories/day
Body Composition
Body Fat %:
Waist-to-Hip Ratio:
WHR Category:
Health Insights
Recommendations
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a widely used screening tool that helps assess whether a person's weight is in a healthy range relative to their height. While not a diagnostic measure, BMI provides a quick snapshot of potential health risks associated with weight. This article explains what BMI is, how to calculate it, and what your results might mean for your overall health.
![]()
What is BMI and Why Does It Matter?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a numerical value derived from a person's weight and height. Developed in the 1830s by Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet, BMI has become a standard tool for classifying weight status and screening for potential health problems associated with weight.
BMI matters because it can help identify potential health risks related to weight. Research has consistently shown that people with high BMI values face increased risks of several conditions, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and joint problems. Similarly, a very low BMI can indicate malnutrition and other health concerns.
BMI is a screening tool, not a diagnostic test. It should be used as one of several assessments of health and wellness, not as the sole determinant.
How to Calculate BMI
The BMI formula differs slightly depending on whether you're using metric or imperial measurements. Here's how to calculate BMI using both systems:
Metric Formula
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height² (m²)
Example: For a person weighing 70 kg and standing 1.75 m tall.
BMI = 70 ÷ (1.75 × 1.75) = 22.9
Imperial Formula
BMI = 703 × weight (lbs) ÷ height² (inches²)
Example: For a person weighing 154 lbs and standing 5'9" (69 inches) tall.
BMI = 703 × 154 ÷ (69 × 69) = 22.7
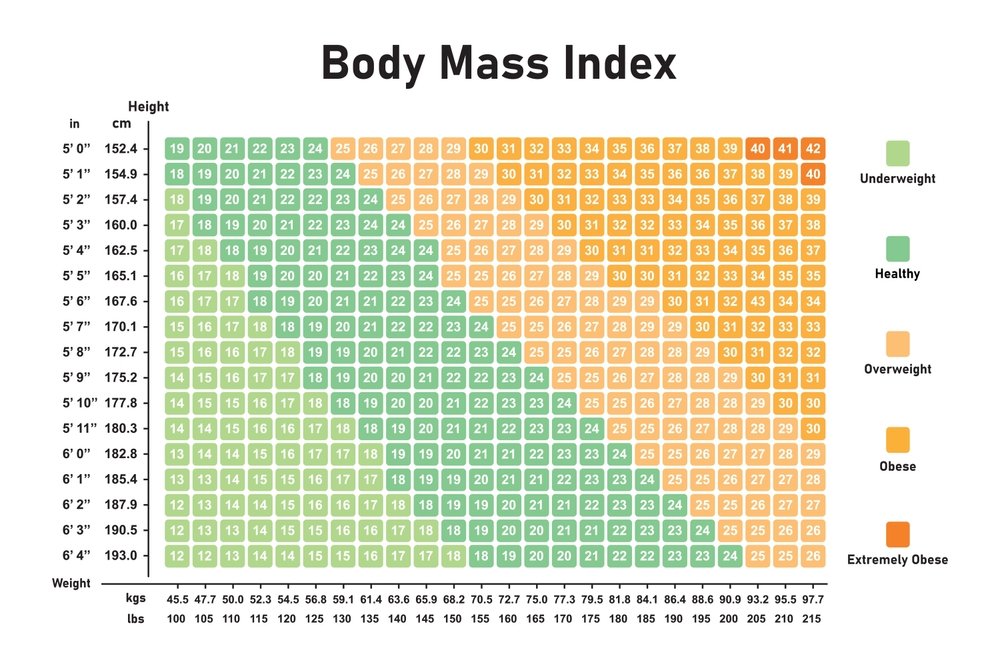
BMI Categories and What They Mean
BMI results are typically categorized into ranges that indicate whether a person's weight might be healthy or potentially problematic. These categories are based on associations between BMI and health outcomes observed in large population studies.
| BMI Range | Weight Category | Health Risk |
| Below 18.5 | Underweight | Potential nutritional deficiencies, osteoporosis, decreased immune function |
| 18.5 to 24.9 | Normal weight | Lowest risk for weight-related health problems |
| 25.0 to 29.9 | Overweight | Increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure |
| 30.0 to 34.9 | Obesity (Class 1) | High risk of weight-related health problems |
| 35.0 to 39.9 | Obesity (Class 2) | Very high risk of weight-related health problems |
| 40.0 and above | Obesity (Class 3) | Extremely high risk of weight-related health problems |
These categories are based on guidelines from the World Health Organization (WHO) and are generally applicable to adults aged 20 and older. Different criteria may apply to children, teens, older adults, and certain ethnic groups.
Benefits of Using Our Online BMI Calculators
While you can calculate BMI manually using the formulas provided earlier, online BMI calculators offer several advantages:
Convenience and Speed
Online calculators eliminate the need for manual calculations, providing instant results with just a few inputs. This saves time and reduces the chance of mathematical errors.
Additional Information
Many online BMI calculators provide supplementary information beyond the basic BMI value, such as healthy weight ranges, percentile rankings, and personalized recommendations based on your results.
Tracking Over Time
Many online calculators allow you to save your results and track changes in your BMI over time, helping you monitor progress toward health goals.
Multiple Measurement Systems
Online calculators typically support both metric (kilograms, meters) and imperial (pounds, feet/inches) measurement systems, eliminating the need for conversion.
Limitations of BMI
While BMI is a useful screening tool, it has several important limitations that should be considered when interpreting results:

BMI Limitations
- Doesn't distinguish between fat and muscle: BMI doesn't differentiate between fat mass and lean mass (muscle, bone, organs). Athletes and muscular individuals may have high BMI values despite having healthy body fat percentages.
- Ignores body fat distribution: BMI doesn't account for where fat is stored in the body. Abdominal fat (around the waist) poses greater health risks than fat stored in other areas.
- Doesn't consider age: Body composition naturally changes with age. Older adults typically have more body fat than younger adults with the same BMI.
- Ethnic variations: Different ethnic groups may have different body compositions and health risks at the same BMI level. For example, Asian populations may face increased health risks at lower BMI values.
- Not suitable for certain groups: BMI may not be appropriate for pregnant women, competitive athletes, or people with certain medical conditions.
"BMI is a useful screening tool, but it's just one factor in evaluating health. A comprehensive assessment should include other measurements like waist circumference, body composition analysis, and consideration of lifestyle factors."
Alternative Measurements to Consider
Due to the limitations of BMI, health professionals often recommend using additional measurements for a more comprehensive assessment:
Waist Circumference
Measuring your waist circumference can help assess abdominal fat, which is linked to higher health risks. For most adults, health risks increase with a waist measurement of over 40 inches (102 cm) for men and over 35 inches (88 cm) for women.
Waist-to-Height Ratio
This ratio is calculated by dividing your waist circumference by your height. A ratio of 0.5 or less is considered healthy. This measurement accounts for height differences and may be more accurate than BMI for some populations.
Body Fat Percentage
Measuring actual body fat percentage provides more precise information about body composition. Methods include skinfold measurements, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and DEXA scans, each with varying levels of accuracy.
What to Do With Your BMI Results
Once you've calculated your BMI, you might wonder what steps to take next. Here's some guidance based on different BMI categories:
If your BMI indicates you're underweight (below 18.5)
Being underweight can lead to nutritional deficiencies, weakened immune function, and other health problems. Consider:
- Consulting with a healthcare provider to rule out underlying medical conditions
- Working with a registered dietitian to develop a healthy weight gain plan
- Focusing on nutrient-dense foods that provide healthy calories
- Incorporating strength training to build muscle mass
If your BMI falls in the normal range (18.5-24.9)
A BMI in this range suggests your weight is appropriate for your height. To maintain this:
- Continue balanced eating habits and regular physical activity
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week
- Have regular health check-ups to monitor overall health
- Consider other health metrics beyond BMI
If your BMI indicates you're overweight (25.0-29.9)
This range suggests increased risk for certain health conditions. Consider:
- Discussing your results with a healthcare provider
- Assessing other risk factors like waist circumference and family history
- Making gradual changes to diet and physical activity levels
- Setting realistic goals for weight management (5-10% reduction can significantly improve health)
If your BMI indicates obesity (30.0 or higher)
This range is associated with higher risk for many health conditions. Consider:
- Scheduling a comprehensive health assessment with your healthcare provider
- Discussing medical and lifestyle approaches to weight management
- Working with specialists like dietitians and exercise physiologists
- Setting small, achievable goals rather than focusing on dramatic weight loss
- Being screened for weight-related health conditions

Remember: BMI is just one screening tool. A healthcare provider can help you interpret your BMI in the context of your overall health, family history, lifestyle, and other factors. Never make significant changes to your diet or exercise routine without consulting a healthcare professional.
Conclusion: BMI as Part of Your Health Journey
Body Mass Index serves as a valuable starting point for conversations about weight and health. While it offers a quick and accessible screening method, it's important to remember that BMI is just one piece of the health puzzle.
A truly comprehensive approach to health assessment considers multiple factors, including but not limited to BMI, waist circumference, physical activity levels, dietary patterns, family history, and other health metrics. By understanding both the value and limitations of BMI, you can use it as one tool among many to monitor and improve your overall health.
Whether your BMI falls within the "normal" range or outside of it, the most important step is to work with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized approach to health that considers your unique circumstances, goals, and needs.